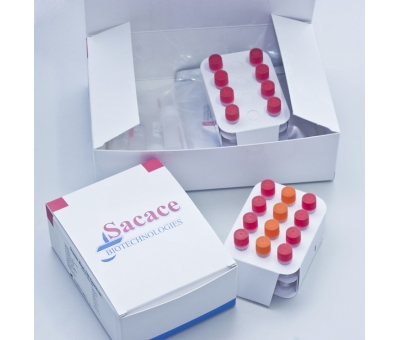
Congo Crimea Real-TM 50 tests
Available on backorder
Expiry Date
Real Time PCR test for detection of Congo Crimea Virus
EGP 18,543.70 EGP 23,179.62
Available on backorder
Infectious diseases are disorders that are caused by organisms, usually microscopic in size, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites that are passed, directly or indirectly, from one person to another. Humans can also become infected following exposure to an infected animal that harbors a pathogenic organism that is capable of infecting humans.
Infectious diseases are a leading cause of death worldwide, particularly in low income countries, especially in young children.
Three infectious diseases were ranked in the top ten causes of death worldwide in 2016 by the World Health Organization. They are lower respiratory infections (3.0 million deaths), diarrheal diseases (1.4 million deaths), and tuberculosis (1.3 million deaths). HIV/AIDS, which was previously on the list, has dropped from the global list of the top ten causes of death (1.0 million deaths in 2016 compared with 1.5 million in 2000), but it is still a leading cause of death in low income countries. Another infectious disease, malaria, accounts for a top cause of death in low income countries.
Based on 0 reviews
Be the first to review “Congo Crimea Real-TM 50 tests”
Shipping Policy
Payment & Delivery:
- You agree to provide valid shipping address, Email address and phone numbers, if we received false information, we are not responsible to any action happen to the product delivered.
- Delivery period may be not known as each item has its own delivery period as well as the seller delivery terms are not the same, so we don't share exact delivery period before we get confirmed information concerning this part, you don't need to confirm your order before receiving such information.
- Some items will have certain Expiry dates, if this information is available on the item, we will share it, if not, please request the expiry date after adding the item to the cart.
- Some items have expiry date that you don't satisfied with, So Please request new expiry date to the same item.
- When placing an order, you will confirm your personal information, shipping and billing address, payment methods, and the subtotal amount of the order.
- You will receive an email confirming your order with your order number, if you wish to contact support you will need to use the specific order number.
- Payment methods are the following:
A- Online payment with credit card (we accept Visa and MasterCard )
B-Cash Upon Delivery
C- Bank deposit in our bank account
- You agree to provide valid and accurate payment information.
Refund Policy
- The buyer has the full rights to return products that are shipped from BGENZ.com.
Cancellation / Return / Exchange Policy
Return Policy:
- The buyer has the full rights to return products that are shipped from BGENZ.com.
- Products can be returned within 14 days of receipt of shipment in most cases.
- Some products have different policies or requirements associated with them.
- Some kits or reagents will need technical report with pictures showing the defect or malfunction.
- You have the right to choose to replace the product or refund your money.
General Inquiries
There are no inquiries yet.



There are no reviews yet.